













http://www.cs.indiana.edu/~gasser/AAU11
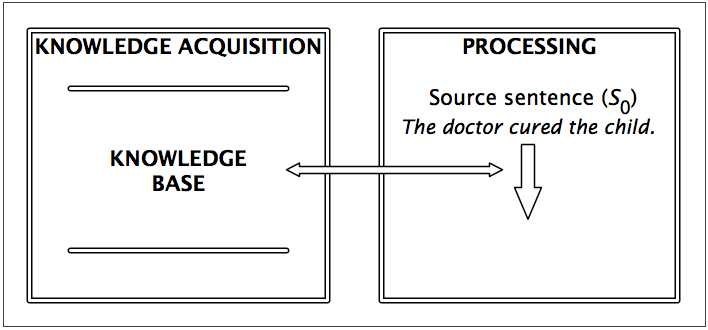
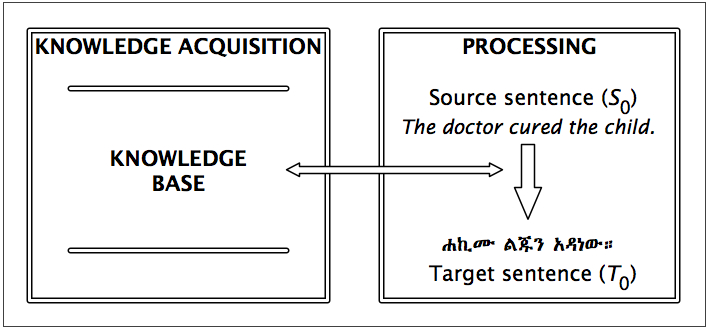
| Vs | → | Vt |
| Sbjs | → | Sbjt |
| Objs | → | Objt |
| I hear her | እሰማታለሁ |
| they hear me | ይሰሙኛል |
| we hear her | እንሰማታለን |
| when you (sg.mas.) hear them | ስትሰማቸው |
| if you (pl.) hear us | ብትሰሙን |
| even if you (sg.fem.) don't hear him | ባትሰሚውም |
| so that I don't hear you (pl.) | እንዳልሰማችሁ |
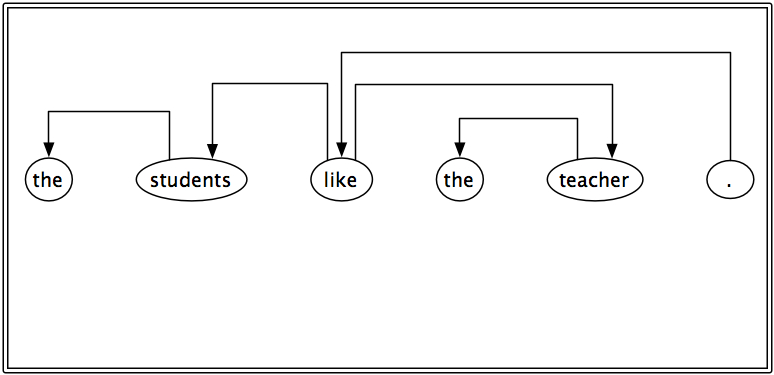
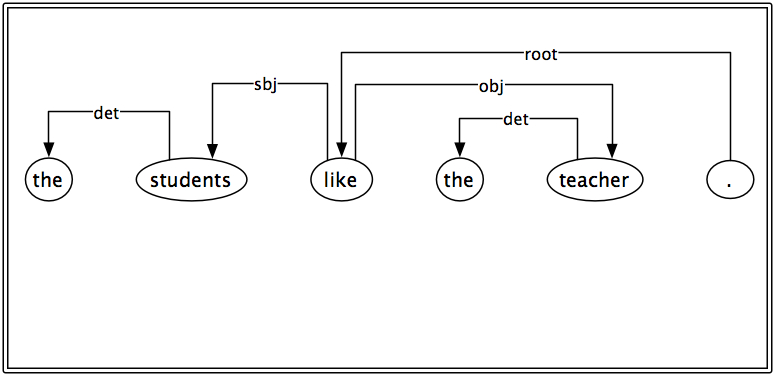
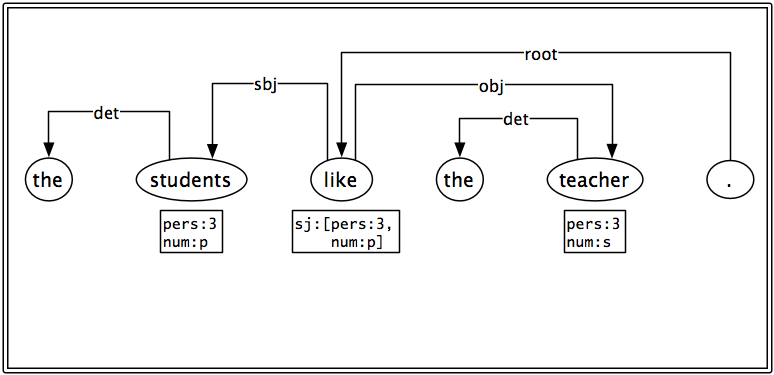
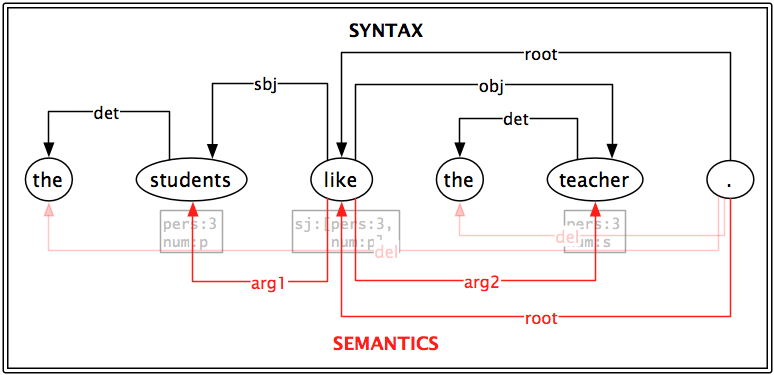
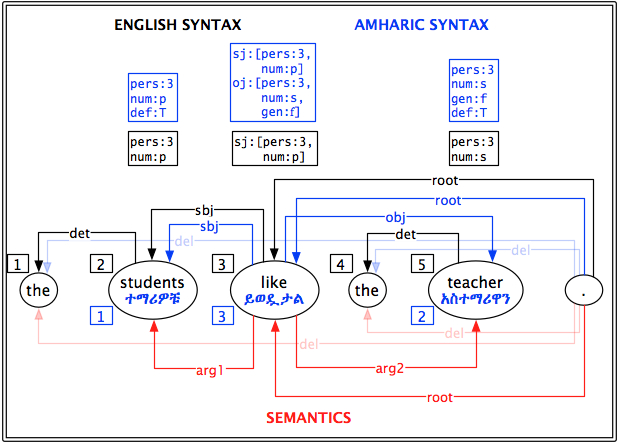
V_T
syn:
out: {sbj: !, obj: !}
synsem:
link: {arg1: sbj, arg2: obj}
~V~like
classes: [V_T]
sem:
lex: LIKE